0 导语
分布式控制在近年来成为了解决微电网中电源广泛接入的协同运行问题的重要研究方向。虽然分布式控制有效降低了通信需求,但是通信过程中不可避免的时延仍会对其控制性能产生较大影响。现有的分布式控制方法缺乏对于通信时延的考虑。为此,本文首先研究了现有方法在时延下的控制效果,进一步提出了一种优化控制方法,实现了时延下精确的电压和功率控制效果。
A Novel Secondary Optimal Control for Multiple Battery Energy Storages in a DC Microgrid
Jianyu Zhou, Mengxuan Shi, Xia Chen, Yin Chen, Jinyu Wen, and Haibo He
期刊名称:IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid
Abstract
The distributed controller consisted of a voltage controller and a power controller is commonly employed on the secondary control layer in the DC microgrid. In this paper, a novel optimal control based on the PI consensus algorithm is proposed for multiple battery energy storages (BESs) in an islanded DC microgrid. Compared with the conventional distributed voltage controller, the proposed scheme improves the system robustness to time delays. The steady-state analysis is conducted to verify that the proposed scheme can take effect in case of time delays. The impact of the secondary controller on the dynamics of the system under time delays is investigated by the eigenvalue analysis. Simulation results confirm that favorable power sharing and DC voltage regulation as well as robustness to time delays achieved by optimal control in an islanded microgrid with multiple BESs and constant power load (CPL).
1 项目背景
由于光伏发电系统,储能装置和直流负载的应用越来越多,直流微电网在未来实现可再生能源分布式接入方面表现出了很大的潜力。储能装置可以有效平抑可再生能源和负荷的随机波动,维持直流微电网的稳定运行。为了实现多储能装置的高效利用,协调控制必不可少。分布式控制通信需求低,灵活性强,近年来被提出以用于解决多储能装置的协同控制问题。
2 论文所解决的问题及意义
现有的分布式控制在存在通信时延时存在控制精度不足的问题,本文提出了一种先进的二次优化控制方法。介绍并分析了其在时延下的稳态控制结果与动态特性,结果表明所提方法能够在时延下精确实现控制目标。同时分析了控制参数对控制性能的影响,可以用于指导控制参数设计。
3 论文重点内容
1) 二次优化控制方法
当前微电网广泛采用分层控制结构。所提二次优化控制属于二次控制,将对一次下垂控制的运行点进行修正以实现稳态时精确的电压恢复和功率分配。各储能装置交换电压信号和电流信号实现全局的控制效果。通过引入额外的通信变量,时延对于控制器稳态控制精度的影响被消除。
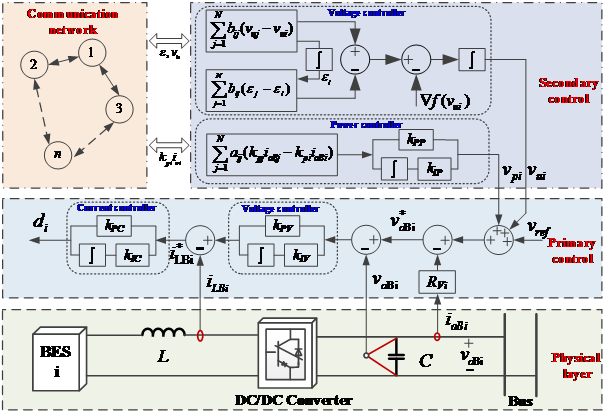
图1 分层控制结构
2) 控制器动态特性
建立全系统含时滞的线性化小信号模型,采用谱离散方法得到时滞系统特征值的数值估计。分别绘制了电压系数g和时滞τ变化下系统的根轨迹,基于此分析了其对系统动态特性的影响。电压系数增大可以在一定程度上加快控制器收敛。时滞增大,系统的动态性能会变差直至失稳。
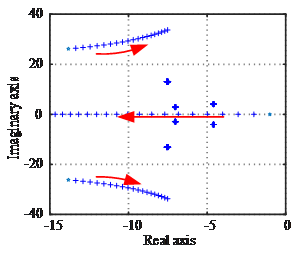
(a)电压系数g:1~20

(b)时滞τ:1~400ms
图2 时滞系统根轨迹
3) 仿真验证
对所提二次优化控制器进行仿真验证。仿真系统包含三组储能装置,相邻的储能装置的通信过程引入了1ms的时延。系统在4s时投入二次控制,在8s时突增负荷。电压的指令值为400V,电流分配比率1:2:3。对比图3和图4可以得出结论,所提控制方法在存在时延时仍能够有效将电压控制在指令值附近。

图3 系统电压电流(现有)
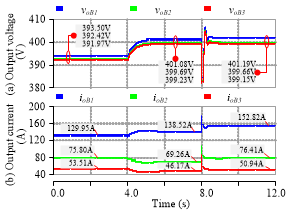
图4 系统电压电流(所提)
Conclusion:
This paper proposes a novel optimal algorithm at the secondary control level to tackle voltage regulation and power sharing among BESs in an islanded DC microgrid.
(1) The global voltage control issue in the DC microgrid is treated as an optimization problem. The optimal control can restore the bus voltage deviation caused by droop control and realize favorable power sharing among BESs.
(2) The optimal controller shows stronger robustness to time delays. Both theoretical analysis and simulations are conducted to verify that the optimal controller can still achieve the control objective in a certain time delay margin.
(3) The impact of the voltage coefficient and the time delay on the system stability and controller performance is revealed. The results can provide guidance to the parameter design.
引文信息
J. Zhou, M. Shi, Y. Chen, X. Chen, J. Wen and H. He, "A Novel Secondary Optimal Control for Multiple Battery Energy Storages in a DC Microgrid," in IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, doi: 10.1109/TSG.2020.2979983.
(https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9034526)
作者简介:周建宇(1995),男,博士研究生,研究方向为微电网运行控制、复合储能技术、分布式算法等,zhoujy@hust.edu.cn。
期刊简介:IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid,一区期刊,2018年影响因子10.486。期刊主要关注智能电网发电、输电、配电和用电相关的原创理论及应用研究。